JMeter is a Java based
desktop application that can be used for performance testing of
different kinds of client-server applications like websites, web
services, databases, FTP servers etc. It is an open source tool
provided by Apache without licensing cost.
The
following types
of applications that can be tested by Jmeter
-
Websites - HTTP and HTTPS
-
Web Services - REST and SOAP
-
Database Servers
-
FTP Servers
-
LDAP Servers
-
Mail Servers - SMTP, POP3, IMAP
-
Shell Scripts
-
TCP Servers
JMeter simulates a group of
users sending requests to a target server, and return statistics that
show the performance/functionality of the target server / application
via tables, graphs etc. The figure below depicts this process:
Assertions are used to perform some validations to check the correctness of the response received from the server.
Listeners in JMeter are used to save, view and analyze the test results in graphical or tabular forms.
We can launch the Samplers in JMeter by following the path-
Critical Section Controller
Aggregate Graph
Constant Timer
The assertions are also helpful in doing functional testing of different kinds of applications by comparing the actual and expected output.
Response Assertion
BeanShell PreProcessor
Post Processors :
Regular Expression Extractor
 x
x
Advantages
of JMeter
-
Free of cost- It is an open source product with zero licensing cost.
-
Can load test different kinds of- It can be used for performance testing of all kinds of applications ranging from - Web applications, web services, database, LDAP, shell scripts etc.
-
Platform independent- As JMeter is 100% Java based, so it is platform independent and can run in multiple platforms.
-
Record and Playback feature- JMeter provides record and playback option along with drag and drop feature which makes it easier and faster to create scripts.
-
Customizable- Since JMeter is open source, developers can customize its source code as per their specific requirements.
-
Supports distributed load testing- JMeter supports distributed load testing feature in which we can create master-slave setup for carrying out load test on multiple machines.
-
Good community support- JMeter has many online tutorials and helping community support. It also has freely available plugins that help in different aspects of script creation and analysis.
Jmeter
Download & Installation
To
install
or rather setup JMeter on Windows, Linux and Mac. Since JMeter is
Java based, so it runs all the operating systems that are Java
compliant. Just make sure your machines has latest version of Java
(JVM) installed.
For
Windows Machines
>
How to download Jmeter:
To
download jmeter we have to access to the following url from web
step
1:
Download the JMeter binary - "apache-jmeter-{version}.zip"
from Binaries section
>
How to Install Jmeter:
step
2:Unzip
the JMeter binary to a directory where we want JMeter to be
installed.
Step
3:
Now we can launch JMeter by double clicking the jmeter.bat file
inside the bin folder.
For
linux Machines
>
How to download Jmeter:
To
download jmeter we have to access to the following url from web
srep
1:
Download the JMeter binary – "apache-jmeter-{version}.tgz"
from Binaries section
>
How to Install Jmeter:
step
2:Extract
the binary to a directory where we want JMeter to be installed.
Step
3:
Now
we can launch JMeter by executing(double clicking) the jmeter.sh file
inside the bin directory.
How
to run jmeter :
Irrespective of machines we
can run jmeter in two ways . Those are one is GUI mode and second one
is Non-GUI mode.
For GUI mode just follow above
steps to run jmeter.
For Non-GUI mode we have to
run from command prompt (Windows) / Terminal (linux).
The following are the
advantages if we run the jmeter in non-gui mode.
-
Increasing threads (after certain limit) due to which JMeter crashes in the GUI mode.
-
For heavy test scenarios (ex: shopping application: login-view product-add to cart-view bill-remove product-pay bill) JMeter consumes memory and CPU and it may affect your test results.
-
To increase JMeter capabilities, i.e. to get more requests per second.
Running
JMeter in command line mode: (windows)
Running JMeter using command
line in non-GUI mode is very simple.
-
Open command prompt
-
Go into JMeter’s bin folder
-
Enter following command, jmeter -n –t test.jmx -l testresults.jtl
JMeter has several parameters
that can be used for running in the non-GUI mode.
-n: It specifies JMeter is to
run in non-gui mode
-t: Name of JMX file that contains the Test
Plan
-l: Name of JTL(JMeter text logs) file to log results
-j:
Name of JMeter run log file
-R: list of remote servers
-H: proxy server hostname or
ip address
-P: proxy server port
Once the test got completed to
see the test results from “.jtl” file , follow the following
steps.
-
Open JMeter in GUI mode.
-
Add any listener Eg. View Results Tree.
-
Click Browse button of the file name field in listener.
-
Open testresult.jtl file.
-
You should be able to see the result in listener now.
Running
JMeter in command line mode: (Linux)
Step 1: open the terminal and
eneter the command
for understanding perpouse i
am giving two ways of commands
simple
command:
jmeter -n -J
jmeter.save.saveservice.timestamp_format="yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss"
-t AFCS_UPDATED.jmx -l result.jtl
complicated
command:
/home/madhusudhana/Desktop/apache-jmeter-5.1.1/bin/jmeter
-n -Jjmeter.save.saveservice.timestamp_format="yyyy/MM/dd
HH:mm:ss" -JAFCS.Threads=100 -JAFCS.RampUp=60
-JAFCS.Duration=900 -JLoop_Controller_login=1
-JLoop_Controller_update_ticket=1 -JLoop_Controller_update_location=1
-t /home/madhusudhana/Desktop/Updated_AFCS/AFCS_UPDATED.jmx -l
Chatak_AFCS_23_MAY_Duration_15min_100TC_60R_1.jtl
Note:
-
To open the jmeter from terminal we have to enter the path where is the jmeter file is available: (the path)
/home/madhusudhana/Desktop/apache-jmeter-5.1.1/bin/jmeter
-
-n --------- indicates that executing in non gui mode
-
time stamp format (same for all the scripts)------------------- J jmeter.save. saveservice.timestamp_format="yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss"
-
-t ------------------ we have to enter the name and path of jmeter jmx file (AFCS_UPDATED.jmx)
-
-l --------------------- we have to enter the name and path of .jtl file where jmeter need to save the jtl file.
Test
plan :
A Test Plan is a logical
container that contains different requests or operations required to
create a performance test script. The different types of operations
are carried out by different elements of the Test Plan. Using JMeter
GUI for adding, removing and configuring the Test Plan elements.
The following are the few of
the commonly used test plan elements
-
Thread GroupThread Groups are used to simulate virtual users in a performance test. We can have multiple thread groups simulating different types of operations performed by users on an application.
-
SamplerSamplers are the different requests which we can send to the server being tested. JMeter provides us various samplers like - HTTP, FTP, TCP, JDBC etc request samplers.
-
Logic ControllersLogic controller allow us to customize the way the Sampler requests is sent to the server. A common example of Logic Controller is Loop controller which makes a request multiple times to the server.
-
Timers
-
Assertions
-
Listeners
-
Config elements
Config elements in JMeter are
used to configure or modify the sampler requests made to the server.
These elements are added at the same or higher level of the samplers
that we want to configure.
Note
:
The
test plan should have atleast one thread group.
Thread
Group:
A Thread Group in JMeter
represents a pool of virtual users performing a set of operations.
For example, considering Google search scenario, one set of users
will be using the search by text functionality, others will be using
News Search, some other smaller section of users might be using
search by image functionality. While creating a performance test
script, for all these users, we will create different Thread Groups
in JMeter with different thread count. The different types of
Samplers like HTTP requests are added as child of these Thread Group
elements to simulate the requests made by users to the server.
To launch the Thread Group in
JMeter by following the path-
step 1: Right Click on Test Plan
step 2: choose Threads(Users)
step 3:Click Thread Group
After
performing those steps we can see the following interface
Thread
Group Properties
The Thread Group element has
a control panel(right pane) that can be use to configure the various
parameters in a performance test like - number of virtual users to
generate, scheduling of the test, introducing of delays in the test
etc.
Name
-
This
is the name of the Thread Group, signifying the action performed by
the virtual users e.g. if a Thread Group is scripted to perform login
operation then we can have Thread Group name as 'LoginUsers'.
Comments
- This
is basically an optional textbox, that should contain the description
of the action performed by the Thread Group or any other metadata
information.
Configurations inside the
"Action to be taken after a Sampler Error" block are used
to configure the test for actions performed in case of any sampler
error, because of no response from server or any assertion error-
-
Continue - In case of sampler error the test should continue.
-
Start Next Thread Loop - The test continues with next thread execution.
-
Stop Thread - The current thread gets stopped in case of error.
-
Stop Test - The thread is stopped gracefully, completing the current sampler request.
-
Stop Test Now - Abrupt stopping of thread in case of any error.
Configurations inside the
"Thread Properties" block-
-
Number of Threads(users) - The number of virtual users to be simulated.
-
Ramp-up Period(in seconds) - The total amount of time taken to get all the thread started. For example - if we want each thread to be active in 0.5 seconds and there are total of 50 threads, then Ramp Up time should be 50*0.5 i.e. 25 seconds. We will see the benefit of using Ramp-Up period in our coming posts.
-
Loop Count- This is the count of the number of loop iteration performing a set of operations defined inside a thread group.
-
Loop Count Forever- When checked, it disables or overrides the loop count value and causes the loop to run infinitely until manually stopped.
-
Delay Thread Creation until needed - This is used to delay the thread creation till a value specified in this field(in seconds).
-
Scheduler - When checked, the scheduler configurations are enabled(explained below) and considered for scheduling of test at a particular time. Otherwise, the test run as soon as we run the test.
Configurations inside the
"Scheduler Configuration" block-
-
Duration(seconds) - Duration specifies the duration of the test, once reached the test stops.
-
Startup delay(seconds) - On running a Test Script, JMeter will wait for the startup delay specified.
-
Start Time - This field is used to specify an absolute value of system time for starting the test, once the test is run. It is considered only if the above 'Duration' field is empty.
-
End Time - This field is used to specify an absolute value of system time for ending the test. It is considered only if the above 'Duration' field is empty.
Note:
To run the jmeter in non-gui
mode we have to do parametrization for ramp-up , ramp-down , duration
.
For example :
number of
threads---------------------${__P(Threads,50)}
ramp-up
--------------------------------${__P(RampUp,5)}
duration---------------------------------${__P(Duration,120)}
(while writing command to
execute jmeter script in non- gui mode we have to use like
J Threads=100 , J RampUp=60 , J Duration =120 )
Samplers
Samplers in JMeter are added
as child of Thread Groups. These are used to send different types of
request to server. Once, the sampler request is processed by the
server, its response is returned to JMeter and the same can be viewed
and analyzed in terms of different performance parameters like
response time, Hits per second, throughput etc.
step 1 : Right Click on Thread
Group
step 2: navigate to Add
Sampler
step 3 : Click on the
required Sampler
We have many samplers but in
real time we will use only few samplers .
So Now we will disucuss about
those samplers. Those are
HTTP
Request -
Used to send HTTP/HTTPS requests to server. This is the most widely
used sampler for testing Web based applications.
JDBC
Request -
Used
to send SQL queries to a database server.
SOAP/XML-RPC
Request -
Used
to send SOAP requests to a SOAP web service.
Flow
control Action -
This
is special type of Sampler, which doesn't send a request to the
server instead it is used to introduce pauses in a test.
FTP
Request -
Used to send file put and get requests to an FTP server.
Apart
from the above defined samplers, there are additional list of
samplers provided by Jmeter- AJP/1.3 Sampler , Access Log Sampler ,
BSF Sampler ,BeanShell Sampler , Debug Sampler , JMS
Point-to-Point,JMS Publisher ,JMS Subscriber,JSR223 Sampler,JUnit
Request, Java Request,LDAP Extended Request,LDAP Request,Mail Reader
Sampler,OS Process Sampler ,SMTP Sampler,TCP Sampler ,Test Sampler ,
WebService (SOAP) Request
In case If are selected the sampler as HTTP
request
then interface look like the following screenshot.
Configeration inside of
HTTP request with an example:
Now
i am going to build a HTTP request for one API.
The
body of the above API is
{
"name":
"PTO Name",
"organizationName":
"RIL",
"organizationId":
"01",
"email":
"pto@girmiti.com",
"state":
"Karnataka",
"city":
"Bangalore",
"country":
"Indian",
"contactDetails":
{
"name":
"ABCD",
"phone":
"+9198459845",
"email":
"contact@girmiti.com"
},
"siteURL":
"http://www.test.com",
"status":
"<Opional>"
On
successful request, the API would return the below response
{
"statusCode": "0",
"statusMessage":
"SUCCESS",
"ptoId": "01"
}
Now
we will see how to build the HTTP request .
Before
going to build the request validate that API in postman tool either
it is returing the expected output or not.
step 1: open jmeter
step 2 : change the name to
test plan or keep the same
step 3 : right click on test
plan and add thread group
step 4 : now right click on
thread group and choose sampler as HTTP request.
Now the above screen shot will
appear to you.
Name
:
you can enter any meaning ful name
comment
: u
can enter any or you can leave
Protocol
(HTTP)
: If you are following http then leave the box empty ifnot enter
https in the box.
IP
Address :
192.168.0.181 ( see above API )
port
name:
9080
method
:
identify the method name from postman for the perticular API
path
:
/coreservice/afcservice/core/1/0/createPTO
Parameters
:
If you want to declare or pass any name / passwords you can pass from
here.
Just hit on add tab at the
bottom and add as you required.
Body
data:
copy the body data of the request from the postman and peaste the
same hitting on body data.
Files
upload:
If you wanna upload any files you can upload here.
Logic
Controllers
Logic Controllers are the
Test Plan elements that are used to customize the order of processing
of Samplers and other elements added as child. Primarily, Logic
Controllers are used with Sampler requests to perform various
customization like - altering their order of processing, grouping
them as a single transaction or running the requests in loop
etc.
Steps to launch a Logic Controller-
step1 : Right Click on Thread
Group
step
2: Hover over Add -> Hover Over Logic Controllers
step 3: Click on the required
Logic Controllers
you can also refer the
following screenshot
what
is the need of logic controllers in jmeter is Performance
test scripts are used to simulate the actions of real users. Just
like a real user will perform multiple actions in different fashion
like perform a set of operations sequentially(e.g. navigate from
login page to home page), perform similar types of operations in a
loop(e.g. reading multiple unread mails), perform some random
operations etc. For simulating these different types of actions,
JMeter provides us different types of Logic Controllers which
customize the element processing inside them.
This is a newly added
controller in JMeter. It ensures that the child elements of this
controller are accessed by only one thread at a time.
ForEach
Controller
This controller is used to
perform the requests in loop, based on the values of a set of related
variables.
If
Controller
Using If Controller, we can
specify a condition whether the child element inside it will run or
not based on a condition which should evaluate to true or false.
Include
Controller
The Include Controller can
be used to provide modularity in JMeter. Using this controller we can
add an external .jmx file(a test fragment) to our existing script by
loading the jmx file in the Include Controler's control panel.
Interleave
Controller
Interleave Controller allow
us to pick and execute a single child element out of multiple child
in each loop iteration. For example- if we have three samplers added
as child to an Interleave Controller than the in first iteration it
will pick the first sampler request, in next iteration it will pick
the next one and so on. Once the child elements are over, it again
starts iteration from first element.
Loop
Controller
It allows to execute the
operations specified as child elements in a loop with iteration value
specified in its control panel.
Module
Controller
Using Module Controller, we
can reuse a test fragment(e.g. a sampler) into our script again by
selecting the module from the Module Controller's control panel.
Once
Only Controller
The once only controller is
used in situation where we would like to perform an operation only
once even if the operation is executed in a loop.
Random
Controller
It is similar to random
controller and picks a single child element in each iteration but
unlike Interleave controller it picks the child element randomly.
Random
Order Controller
The Random Order controller
is used to execute each of its child element at most once in a random
order.
Recording
Controller
This controller acts as a
placeholder where the scripts recorded using HTTP Proxy Server are
recorded by default.
Runtime
Controller
Runtime controller is used
to limit the time of execution of its child elements. For example, if
we have specified the value of 'Runtime' as 100 seconds then the
elements inside the Runtime controller will run for 100 seconds with
as much iteration as possible.
Simple
Controller
This controller is just a
placeholder for grouping and ordering the different elements of test
plan.
Switch
Controller
This controller is used to
pick one element for processing out of its multiple child elements.
The element are picked not in sequential order or random order
instead it is based on a switch value defined in its control panel.
The switch value can be an variable with value evaluated to its
index(position) of the element or name of the element. For example,
if in first iteration the switch value is evaluated to '3' then the
fourth element is picked for processing(index value starts from 0).
Similarly, if switch value is evaluated to an element's name then
that element is picked for processing.
Throughput
Controller
The Throughput Controller is
used to control the processing of its child elements in terms of the
total number of executions or the percentage of execution specififed
in its control panel.
Transaction
Controller
The Transaction Controller
is one of the widely used controller in JMeter scripts. It is used to
group multiple sampler requests into one. The response time and other
performance metrics of the test result are evaluated for the whole
transaction. For example - while checking performance of home page of
an application, we can notice that launching the home page generates
numerous requests at the backend. Hence, this requires grouping all
these request into one transaction, for this we have transaction
controller in JMeter. Once we run the script, we can find the overall
response time of the whole transaction.
While
Controller
The While controller is used
to run the child elements inside it till the value specified in its
control panel is evaluated to false.
Listeners
Listeners are the test plan
elements that are used to view and analyze the result of performance
tests in tabular or graphical form. They also provide the different
response time metrices (average time, minimum time, max time etc) of
a Sampler request.
How to add a Listener-
step 1: Right Click on Test
plan
step 2: Listener and choose
the required Listener
you can see the screenshot
below for your reference.
We can add listeners as
child of a particular Thread Group also. In that case, the Listener
will use the data of that Thread Group for analysis.
The Aggregate Graph listener
is used to display the test results in both tabular form(reports) and
graphs.
Aggregate
Report
The Aggregate Report
listener is used to display and store test results in the form of
reports.
Assertion
Results
The assertion results
listener is used to display the assertion result for each erroneous
sampler response. It is advised to not use this listener during
performance test as it is very resource intensive. It should be used
while debugging and functional testing only.
Backend
Listener
The backend listener is a
special type of asynchronous listener used specifically with
BackendListenerClient for its customization.
BeanShell
Listener
The beanshell listener is
used to enable beanshell scripting in Jmeter.
BSF
Listener
The beanshell listener is
used to enable BSF scripting in Jmeter.
Comparison
Assertion Visualizer
The Comparison Assertion
Visualizer is used to provide the comparison between assertion result
in an easy to compare UI.
Generate
Summary Results
The Generate Summary results
listener is used to store and display detailed test results to log
files.
Graph
Results
The Graph results listener
is used to display each sampler request's response time graph in
terms of average, median, deviation and throughput.
JSR223
Listener
The JSR223 Listener is used
to enable JSR223 scripting in Jmeter.
Mailer
Visualizer
The Mailer Visualizer
sampler is used to provide the functionality of sending customized
mails in case of some specific error threshold.
Monitor
Results
This is a newly added
listener in JMeter used to display and store server performance
stats.
Response
Time Graph
The response time graph is
used to provide the graphical representation of response time with
time elapsed during the test run.
Save
Response to a file
The save response to a file
listener is used to store the sampler response in a file. This
listener is used while functional testing or debugging the test
script.
Simple
Data Writer
The simple data writer
listener is used to save the sampler response to a file after with
different configurations to remove several unnecessary overheads.
Summary
Report
The summary report is used
to store and display the test result in tabular form just like
aggregate report listener but consumes less memory(as per Apache
Jmeter).
View
Results Tree
This listener is used to
provide and store test results for each and every individual sampler.
View
Results in Table
The view results in table
listener is used to display the sampler response header and response
body.
Among those listeners commonly
used listners are view reult ,summary report , aggregate and
beanshell.
Timers
Timers are the test plan
elements used to pause the execution of test for a certain specified
amount of time. This pause between requests helps in simulating
real-world scenarios like time taken by users to think, type
something, see and process the information displayed etc.
How to add a Timer-
step
1:Right Click on Thread Group
step 2: choose Add and select
the Timer Click on the required Timer
From the following screenshot
you can see the same.
Types of timers available in
jmeter are Beanshell timer , BSF timer,constant throughput
timer,constant timer,gaussion random timer,JSR223 timer ,poission
random timer , random timer ,random order timer and synchronizing
timer.
The constant timer is one of
the most widely used timers in JMeter. It pauses the execution of
test for a specified constant amount of time.
Uniform
Random Timer
The uniform random timer is
used to pause the test execution for a random time. The maximum value
for random time can be specified along with the additional constant
time with each wait.
Constant
Throughput Timer
The constant throughput
timer is a special type of timer used to create pauses with variable
amount of time while maintaining the overall throughput i.e.
samples/minute.
BeanShell
Timer
The beanshell timer is used
to generate the delays using beanshell scripting.
BSF
Timer
The BSF timer is used to
generate the delays using BSF scripting.
Gaussian
Random Timer
The Gaussian random timer is
used to generate the delays using Gaussian distribution.
Synchronizing
Timer
The Synchronizing timer is
used to insert delays in script by bocking a certain number of
threads and when the blocked thread count reaches a specified number
then the threads are released at once. Since, the synchronizing timer
generates large amount of instant load hence, it is used for spike
testing.
Poisson
Random Timer
The Poisson random timer is
used to generate the delays using Poisson distribution.
JSR223
Timer
The JSR223 timer is used to
generate the delays using JSR223 scripting.
Assertions
Assertions in JMeter are the
test plan elements that are used to validate the response received
from server for a particular sampler request. In order to test a
sampler response, we can add different assertions to the sampler
requests as child. If an assertion fails, the sampler request is
marked as failed and the same gets reflected in the test results
listeners like - aggregate report listener.
Assertions are needed in
performance test scripts to validate that the response received from
server is correct and is not affected by increasing the load on the
server.
How to add an Assertion-
step
1:Right Click on a Sampler Request
step 2: Add Assertion and
Click on the required Assertion
you can see the same in the
screenshot.
The types of assertions in
jmeter are response assertion,duration assertion,size assertion,HTML
assertion,XML assertion ,compare assertion ,JSR223 assertion etc.
The response assertion used
in test scripts to validate a pattern in the response body, header,
code, message etc. There are different pattern matching rules to
validate the response like-
-
Contains - If the response text contains the regular expression to be matched
-
Matches - If the whole response text matches the regular expression
-
Equals - If the whole response text matches the pattern(not regular expression but the pattern string)
-
Substring - If the response text contains the pattern(not regular expression)
-
Not - To check that the pattern is not present in the response text
HTML
Assertion
The HTML assertion is used to
check the HTML syntax of the response.
Size
Assertion
The size assertion is used to
validate the size of the response with a specified value in bytes.
Compare
Assertion
The Compare Assertion is used
to compare sampler results.
BSF
Assertion
The BSF Assertion is used to
validate the sampler result using BSF scripting.
Duration
Assertion
The duration assertion is
used to validate that the sampler request gets processed within a
specified amount of time.
XML
Assertion
The XML assertion is used to
validate that the response follows a valid XML syntax.
XML
Schema Assertion
The XML Schema Assertion is
used to validate the response against a specified XML schema.
XPath
Assertion
The XPath assertion is used
to validate the response using XPath expressions.
MD5Hex
Assertion
The MD5Hex Assertion is used
to validate the sampler result by checking its MD5Hex hashcode
against a hashcode value provided.
SMIME
Assertion
The SMIME Assertion is used
to validate the body of a MIME message.
JSR223
Assertion
The JSR223 Assertion is used
to validate the sampler result using JSR223 scripting.
Config
elements
Config elements are used to
configure or modify the sampler requests made to the server. These
elements are added at the same or higher level of the samplers that
we want to configure.
How to add an Config
elements-
step 1:Right Click on either of Test Plan/Thread
Group/Logic Controller
step 2:Hover over Add choose
Config Element and Click on the required Config Element
for reference you can see the
following screenshot.
The config elements are
counter,csv data set config,FTP request default,HTTP header manager
,HTTP cookie manager,Login config element,random variable,user
defined variable,HTTP header request defaults , JDBC request defaults
etc.
CSV
Data Set Config
The CSV Data Set Config is
used to read data from CSV file, put the data into variable(s) and
then use the variable(s) in the sampler requests.
HTTP
Cache Manager
The HTTP Cache manager is
used in test scripts to add the Caching functionalities of web
applications. This element is just required to be added at same level
or higher than the sampler request where caching functionality is
required.
HTTP
Cookie Manager
The HTTP Cookie manager is
required to for session handling by providing functionality of
storing and sending of cookies.
User
Defined Variables
As the name suggests, the
User Defined Variable config element is used to create variables with
a value (key-value pairs) that are used across the test script.
Random
Variable
The random variable config
element is used to generate random numeric values within a range of
specified minimum and maximum values.
Counter
The counter config element
is used to create a variable that gets incremented by a specified
value in each iteration within a range of minimum and maximum values.
JDBC
Connection Configuration
JDBC Connection
Configuration is used with JDBC request sampler to create JDBC
connection settings.
FTP
Request Defaults
The FTP request defaults are
used to create default settings while testing FTP servers.
DNS
Cache Manager
The DNS Cache Manager is
used while testing applications behind the load-balancers.
HTTP
Authorization Manager
The HTTP Authorization
Manager is used for testing applications requiring multiple logins
for ensuring authorization.
HTTP
Request Defaults
The HTTP Request Defaults
config element is used for setting default values for HTTP requests.
HTTP
Header Manager
The HTTP Header Manager is
used to override the HTTP request headers.
Java
Request Defaults
The Java request defaults
config elements is used to specify default values for Java Request
sampler.
Keystore
Configuration
The Keystore Configuration
config element is used to configure the loading of keystores.
Login
Config Element
The logic Config element is
used to create default credentials for the samplers using username
and password in their setup
LDAP
Request Defaults
The LDAP request defaults
are used to create default settings while testing LDAP servers.
LDAP
Extended Request Defaults
The LDAP extended request
defaults are used to create default settings for LDAP Extended
Request samplers.
TCP
Sampler Config
The TCP Sampler Config is
used for creating default settings for TCP Sampler.
Simple
Config Element
The simple config element is
used to create key-value pairs that can be used across the test
script.
Pre
Processor elements
The Pre Processor elements
are used to modify the sampler requests before their processing(hence
the name pre-processor).
How to add a Pre Processors in
JMeter-
step 1:Right Click on either of Thread Group/Logic
Controller
step 2: Add -> Hover Over
'Pre Processors' and Click on the required Pre Processor Element
you can refer the same in the
following screenshot.
The pre processors in jmeter
are beanshell pre processor , BSF preprocessor ,HTML link parser
,JDBC preprocessor , Regex user parameters , sample timed out and
user parameters.
The BeanShell preprocessor
is used to perform some operation using beanshell scripting before a
sampler request.
HTML
Link Parser
The HTML Link Parser is used
to extract links from HTML response fetched from server.
HTTP
URL Re-writing Modifier
The HTTP URL Re-writing modifier
can be added at either Thread Group level or Sampler level
to fetch a specific sessionID parameter from the response of a
request and then use the parameter's value on other requests.
JSR223
PreProcessor
The JSR223 preprocessor is
used to perform some operation using JSR223 scripting before a
sampler request.
JDBC
PreProcessor
The JDBC PreProcessor is
used to execute certain specified SQL queries before a sampler
request processing.
RegEx
User Parameters
The RegEx user parameters
are used to extract HTTP parameters from certain request using a
regular expression and then passed as request parameter to other
sampler requests.
User
Parameters
The User parameters are used
to specify values for User variables used within Thread Groups.
The Post Processors are the
test plan elements that are used to perform certain actions after the
processing of a sampler request. These post processors are usually
used for extracting certain values from the response of a sampler
request e.g. we can extract the value of session variables from an
HTTP request and pass the session variable's value to the subsequent
requests.
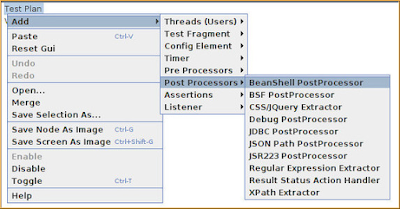
How to add a Post Processor in
JMeter-
step 1:Right Click on either of Thread Group/Logic
Controller
step 2:Hover over 'Add' select
'Post Processors'
step 3:Click on the required
Post Processor Element
You can see the same in the
following screenshot.
The post processors in
jmeter are beanshell ,BSF,CSS/Jquery .Debug,JDBC,JSON path,Regular
expression and Xpath extractor.
Regular Expression Extractor
is the most frequently used post-processor. It is used to extract
values from HTTP response using regular expression and to store the
values to a variable. Then the variable can either be used as request
parameter to other samplers or can be used for other purposes like
assertions, debugging, storing in file etc.
BeanShell
PostProcessor
The BeanShell PostProcessor
is used to perform some operation using beanshell scripting after a
sampler request processing.
CSS/JQuery
Extractor
The CSS/JQuery Extractor is
used to extract values from HTTP response using CSS or JQuery
expressions and then the extracted value is stored in a variable.
XPath
Extractor
The XPath Extractor is used
to extract values from HTTP response using CSS or JQuery expressions
and then the extracted vlaue is stored in a variable
Debug
PostProcessor
The Debug PostProcessor is
used to create a subSample having properties of previous sampler
request, JMeter properties, JMeter variables or system properties.
JSR223
PostProcessor
The JSR223 PostProcessor is
used to perform some operation using JSR223 scripting after a sampler
request processing.
JDBC
PostProcessor
The JDBC PostProcessor is
used to execute certain specified SQL queries after a sampler request
processing.
JSON
Path PostProcessor
The JDBC PostProcessor is
used to extract data from JSON response using JSON-Path syntax.
Result
Status Action Handler
The Result Status Action
Handler is used to stop a thread group or the whole test in case of a
specific sampler failure.
Parameterization
Parameterization is the
technique using which we can execute a test plan multiple times with
different set of data. This helps in creating load test script that
closely simulated real-world scenarios where different users use
different test data.
Suppose, we have to do load test of a
search engine like google. First step will be to record the search
scenario. Now to do effective load test, we can't just playback the
script for say 500 users. We should simulate 500 users that search
for 500 different things. For this we can use parameterization,
wherein we can have a CSV file that contains 500 different search
keywords. Now instead of the static search item that we had recorded
in our script, we can include the search items from the CSV file
dynamically.
In jmeter, one of the common
ways to parametrize your performance scripts is to use a CSV file.
The best example of CSV input files usage is a login process. If you
want to test your application across different users, you need to
provide a list of user credentials.
Let’s assume that we have a
login request that works for one specific user:
The following screenshots
guide you to how to do parameterizatio
Step 1: open jmeter
step 2: add thread group
step 3: add HTTP sampler
step 4: enter all details as
shown in the screenshot like ip address ,port ,method and path and
also peaste the body of the request.
step 5: Now instead of email
and pass we need to pass the parameters.
To achieve this we have to go
for parameterization.
To pass any variable we have
to use this format ---------- ${parameter name}
so here instead of name we
enter ---------${email}
instead
of pass we enetr ----------${password}
screen
shot : 1
screenshot 2:
To pass the parameters we
are using csv data config element .As shown in above screen shot add
csv data congig element to thread group.
Configeration elements in csv
data config element:
step 1 :First prepare the
valid test data i.e. email and passwords and save those in a file
with the extension of a file as “.csv” .Now browse that file path
.
Step 2: leave the file
encoding as it is.
Step 3: we have to enter
variable names as like as how we enetere the column names in csv file
(email , password) with comma or space or tab separated
step 4: hit on the drop down
and choose whether we wanna ignore first line or not.
If we wanna ignore first line
-----------choose TRUE if not choose FALSE.
Step 5 : choose delimeter
either we used the delimeter as space/ camma/tab
step 6: If you wanna allow
quoted data is choose TRUE if not choose FALSE
step 7: If you wanna recycle
the data then choose TRUE if not FALSE
step 8: choose the EOF as
FALSE if you choosen the above as TRUE if not choose FALSE
step 9: sharing mode will be
all threads means ---- All the threads will share the data from csv
file
If you choose current
thread----- Apply only for perticulat thread only.
Note:
To
know whether the data is passing as parametere or not we can check by
adding listner.
Step
1: Add the listner (view result tree)
step 2: run the test
step 3: Hit on the view result
tree
step 4: hit on request.
Now as shown in the below
screenshot the parametrs are passed instead of email and password.
Correlation
Correlation
is the most important aspect of scripting. It usually includes
fetching dynamic data from preceding requests/calls and posting it to
the subsequent requests.
Let's
take an example to find out why exactly we need correlation. Suppose
we have recorded a scenario in which-
User
enters login details and click OK button
Home
page opens and user take further actions
Now,
if we just playback this script, the test will fail even for a single
user. This is because of the authentication mechanism used. When we
login to a website, session variables are dynamically created. These
session variables are passed to the subsequent requests and help
validation & authentication of the actions performed. So, one
cannot just record and playback the requests having these variables.
Here, we need to correlate the web requests with the dynamic
variables. And for correlation, we need to use the "Regular
Expression Extractor" which makes use of regular expressions.
So, before going deep into Correlation, let's first understand
"Regular Expressions".
Regular
expression
Regular
expressions are used to fetch data from a string based on a search
pattern. Basically, in order to extract any value (generally a
dynamically created value) from a string response, we define a left
bound of the variable then some wildcard characters and then a right
bound-
(leftbounday)
(body to be capture) (right bounday)
For
example : The server is returning the session id for login request .
we wanna capture that session id .For that we have to use
regexpression extractor
server
returing value is
session
id =”1e234323254343464”/>?
Left
boundary = session id=”
body to
capture = 1e234323254343464
right
boundary = ”/>?
If we
use the above expression every reply the expression will extyract the
server return value.
Where
“.
“- match any character
“+”
- one or more times
“?
“- stop when first match succeeds
Steps
to follow to capture dynamic value:
step 1:
open jmeter
step 2:
Add thread group
step 3:
add sampler
step 4:
Add regular expression extractor
From the
following screen shot you can find more details.
Configeration
elements in regular expression:
Name
:
you can give any meaning ful name as a name.
Name
of created value :
give any meaning full name but to use extracted / dynamic value some
where at that time we have to use same name as a parameter.
Regular
expression:
here we have to peaste the regular expression which is formed by you.
Templet:
here enter the posion of occurence of the dynamic value (ex : if it
is first occurance then give like $1$)
Match
no :
If you wanna pick random number then give 0 if not leave blank.
Data
Base Tesing (JDBC Request)
Using
JDBC request sampler we can test the database.
Steps to
do the database testing.
Step 1:
open jmeter
step 2:
add thread group to test plan
step 3 :
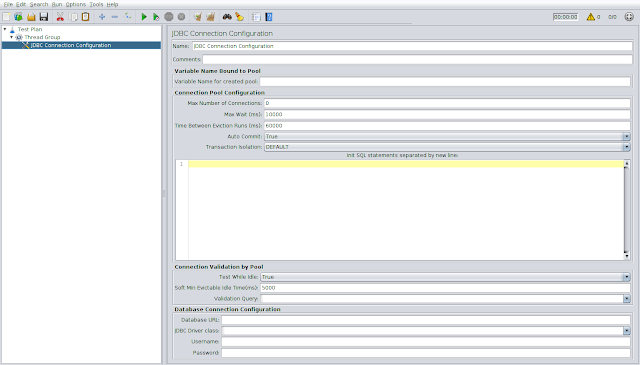
Add the config element (JDBC connection cofig)
( see
the following screenshot for reference.)
The Config Element- "JDBC
Connection Configuration" is required to be added as child of
the Thread Group. The properties in "Connection Pool
Configuration" and "Connection Validation by Pool" can
be kept with default values. Appropriate values for the following
parameters need to be configured in "Database Connection
Configuration" section-
-
Database URL - The URL of the database server
-
JDBC Driver class - The database driver name e.g. com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
-
Username - The username of the user having access to run the SQL query in the database
-
Password - The password of the user having access to run the SQL query in the database
step 4:
Add JDBC request sampler.
(see
the following screenshot)
The
Sampler- JDBC Request needs to be added as child of the Thread Group
below the JDBC Connection Configuration. Here we can select the type
of SQL query form the "Query Type" drop-down and place the
SQL query in the "Query" text field.
Step 5:
Add the listeners . ( To know the output we have to add the listeners.)
Step 6:
add assertion also if you want. (For validation)
step 7:
Run the test.
FTP
request sampler
The
following steps we have to follow to test the FTP server.
Step 1:
open jmeter
step 2:
add thread group to test plan
step 3:
add config element as FTP request defaults. ( see the following
screen shot)
we have
to enter configuration details .
The
Config Element- "FTP Request Defaults" is required to be
added as child of the Thread Group. Here you can add configure
default properties that can be used by multiple "FTP Request
sampler" like FTP server name, port, remote file, local file,
mode etc.
Step 4:
Add the sampler FTP request (see the below screenshot)
Enter
all the configuration elements as like as FTP request config element
but additionally we have to enter credentials ( user name and
password) to connect to the FTP server.
Step 5:
Add the listeners . ( To know the output we have to add the listeners.)
Step 6:
add assertion also if you want. (For validation)
step 7:
Run the test.
Distributed
load testing:
Distributed
load testing is the process using which multiple systems are used for
simulating load of large number of users. In JMeter, this is achieved
by creating a Master-Slave configuration.
The
reason of using more than one system for load testing is the
limitation of single system to generate large number of threads
(users).
For
distributed load testing we need to create Master-slave configuration
wherein
Before
we start,there are a couple of things to check.
-
the firewalls on the systems are turned off.
-
all the clients are on the same subnet.
-
the server is in the same subnet, if 127.0.0.1 ip addresses are used. If the server
-
Make sure JMeter can access the server.
-
Make sure you use the same version of JMeter on all the systems. Mixing versions may not work
-
correctly.
Once
you've made sure the systems are ready, it's time to setup remote
testing. The tutorial assumes you already have JMeter installed on
all the systems. The way JMeter works is 1 master controller
initiates the test on multiple slave systems.
Terminology
Before
we dive into the step-by-step instructions, it's a good idea to
define the terms and make sure
the
definition is clear.
Master
– the system running Jmeter GUI, which controls the test
Slave
–
the system running jmeter-server, which takes commands from the GUI
and send requests to the target system(s)
Target
–
the webserver we plan to stress test
Master
will control all the slaves and collect the test results.
To
make the system work firewall needs to be turned off and all the
systems need to be in same subnet. Also, preferably all the systems
need to use same version of JMeter and Java.
-
First of all we need to start the jmeter-server.bat in the slave systems. For this just go to the bin folder inside JMeter home directory and run the batch file jmeter-server.bat(for windows) or jmeter-server (for linux).
-
Now on the master system open the properties file jmeter.properties and edit the remote_hosts entry. Remove the loopback address's value (127.0.0.1) for the remote_host entry and specify the IP addresses of all the slave systems separated by commas.
In the
following screen shot you can see initially only one url is there.
Now i am adding two more hosts under remote hosts and configeration . You can see the same in the below screenshot
Like
this you can add the hosts as many you want.
Starting
the Test
At
this point, you are ready to start load testing. If you want to
double check the slave systems are working, open jmeter.log in
notepad. You should see the following in the log.
Jmeter.engine.RemoteJMeterEngineImpl:
Starting backing engine
If you
do not see this message, it means jmeter-server did not start
correctly. For tips on debugging the issue, go to the tips section.
There are two ways to initiate the test: a single system and all
systems.
How
to Start a single server
step1. click Run at the top
step2. select Remote start
step3. select the IP address
(see the screenshot )
How to start all servers
step1.
click Run at the top
step2. select Remote start all
or use CRTL-Z (see the screenshot)
Saving
the test plan
You can save an entire Test
Plan either by using Save or "Save Test Plan As ..." from
the File menu. Or by default save button will be there in jmeter hit
on that save the script by providing a name .jmx.
Running
a test plan
You can run your Test Plan
choosing Start (Control + r) from the Run menu item. When JMeter is
running, it shows a small green box at the right hand end of the
section just under the menu bar.
The numbers to the left of the
green box are the number of active threads / total number of threads.
These only apply to a locally run test; they do not include any
threads started on remote systems when using client-server mode .
In the following screenshot
you can see the save and run buttons.
Recording
Script with Jmeter
we can record the script using
the jmeter non-test element( Http test script recorder)
Step 1: open jmeter
step 2: add to non test
element (HTTp test script recorder)
step 3:Now in http test script
window,port value will be 8080 by default,otherwise set it to 8080
step 4:In the drop down
list,select recording controller as the target controller.
In the next step,add recording
controller,under http test script recorder.Recording controller
enables to record script under it,so that it will be in a structured
way.
Step 5 :The workbench is now
ready to record scripts.Now open web browser and go to settings.
Step 6:In settings,go to proxy
server and check the check box.
Step 7:Type localhost in the
address text box and in the port provide the port number which we
have given to proxy server port ie 8080.
step 8:Finally click ok button
and close the window.
Step 9:To start recording the
script, type url of the application in the browser and press enter.
Now in recording controller under workbench,some http request will be
recorded. For eg, if the static web site has five pages and if we
want to record those five pages in different group or specified
name,then it can be done.
Step 10:In the next step, add
simple controller to the http test script recorder and select the
entire http request from the recording controller and paste it under
simple controller.
Step 11:Once the recording is
done,go to internet options and uncheck the check box in proxy server
and save it.
Step 12:In the next step,copy
the script to test plan under thread group.
Step 13:Finally, add listeners
to the thread group.Add agrregate grph,view results tree and response
time graph to view the results.
Note:
see
the following screenshot for reference
Execution
order of Test Elements
Following is the execution
order of the test plan elements:
1. Configuration elements
2. Pre-Processors
3. Timers
4. Sampler
5. Post-Processors (unless
SampleResult is null)
6. Assertions (unless
SampleResult is null)
7. Listeners (unless
SampleResult is null)
How
to generate report(HTML format)
GUI
mode:
once
test got completed the results will be stored in a .jtl extension
file.
Step 1:
Navigate to tools and choose generate HTML report (see the following
screenshot)
step 2:
browse the result file (jtl file)
step
3:browse the user.properties file
step 4:
give the path where to generate the html formated file.
Step 5:
hit on generate report
step 6:
Navigate to given output directory for HTML format report file.
Non-GUI
mode
Once
the test was executed in non-gui mode the jtl file will be saved in
the given directory. After the execution follow the below steps to
generate HTML report in non-gui mode.
Step 1:
open the terminal/ command propt
Step 2:
Enter command
for
example :
I
written the following command to generate the report in non-gui mode.
/home/madhureddy/Desktop/apache-jmeter-5.1.1/bin/jmeter
-J jmeter.save.saveservice.timestamp_format="yyyy/MM/dd
HH:mm:ss"
-g
/home/madhureddy/Desktop/Chatak_AFCS_23_MAY_Duration_15min_100TC_60R_1.jtl
-o
/home/madhureddy/Desktop/Chatak_AFCS_23_MAY_Duration_15min_100TC_30R_1
Explanation
for the above example how i written the command:
Analysis
After executing a load test, we need to interpret the test results.
For result interpretation, we use Listeners in JMeter. These
listeners provide different matrices about the load test. In this
post, we will see the most commonly used matrices, their meanings and
the how they are calculated internally from raw data.
Result
matrices by Aggregate Report Listener-
Label-
Label is the name of the sample or the Transaction Controller
Samples
- The total number of samples corresponding to a given sample
Average
- The average time taken (in milliseconds) to execute the requests
under a given label. So, if there are 10 samples getting executed
then average time taken will be-
Average
= Total time taken by all samples /#samples
Median
- The median is basically the middle value of response time in the
sorted list of samples
90%
Line
- The Apache JMeter manual describes 90% line as- "90% of the
samples took no more than this time". It is actually the 90
percentile of the response times of the samples -
90
percentile = (90/100)*N+1/2 where N is the number of samples
So,
if there are 10 samples then 90%line will be 9.5 or 9. It means the
9th value in the sorted list of samples (sorted according to
ascending order of their response times) will be the 90% line
value.
Min
- The minimum time (in milliseconds) taken by the sample
Max
- The maximum time (in milliseconds) taken by the sample
Error
%
- Percentage of errors in the samples
Throughput
- Throughput as we all know is output per unit time. In JMeter terms
we define throughput as the amount of load applied on the server. So,
numerically-
Throughput
= Total number of requests to the server/ Total time
or
Total number of requests to the server/(End time of last sample
-Start time of first sample)
Here
we just defined Total time in which load was applied on the server as
time duration between Start of first sample and end of last
sample.
KB/sec
- The metric KB/sec is nothing but the throughput measured in terms
of bytes. So,
KB/sec
= (Throughput*Average bytes) /1024
Here
Average bytes is the average value of the sample response in bytes
and the term 1024 is used to convert the value (Throughput*Average
bytes) into kilobytes.


























No comments:
Post a Comment